

An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube. This condition is a medical emergency because the pregnancy cannot continue to term and poses serious risks to the woman’s health. The procedure for managing an ectopic pregnancy depends on various factors including the woman’s condition, the location of the ectopic pregnancy, and the extent of damage.
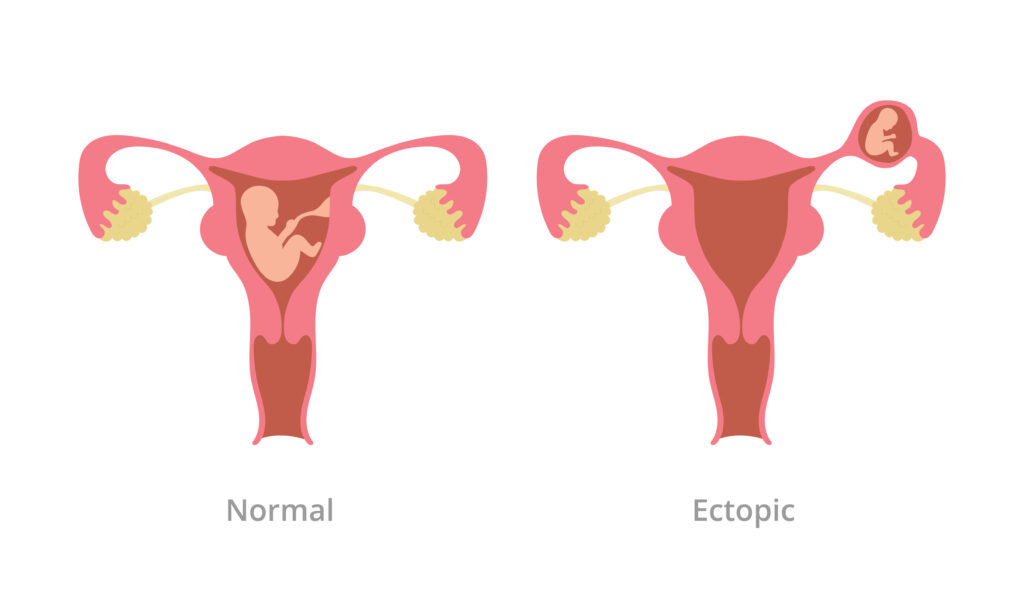
Indications
Surgical intervention for an ectopic pregnancy is necessary when:
Types of Surgical Procedures
Procedure Steps
Risks and Complications
Recovery and Outlook
Conclusion
Surgical management of an ectopic pregnancy is a critical intervention aimed at preserving the woman’s health and fertility. The choice of surgical procedure depends on factors such as the woman’s condition, the location of the ectopic pregnancy, and the extent of damage to the fallopian tube. Advances in surgical techniques, including minimally invasive approaches, have improved outcomes and recovery times for many women undergoing surgery for ectopic pregnancy. Regular follow-up care is essential to monitor healing and address any concerns that may arise during recovery.