

Uterine fibroids surgery, also known as myomectomy or hysterectomy depending on the case, involves the surgical removal of fibroids—non-cancerous growths that develop in the uterus. The choice of surgery depends on factors such as the size, number, location of the fibroids, and the patient’s symptoms and desire for future fertility. Here’s an overview of surgical options for uterine fibroids:
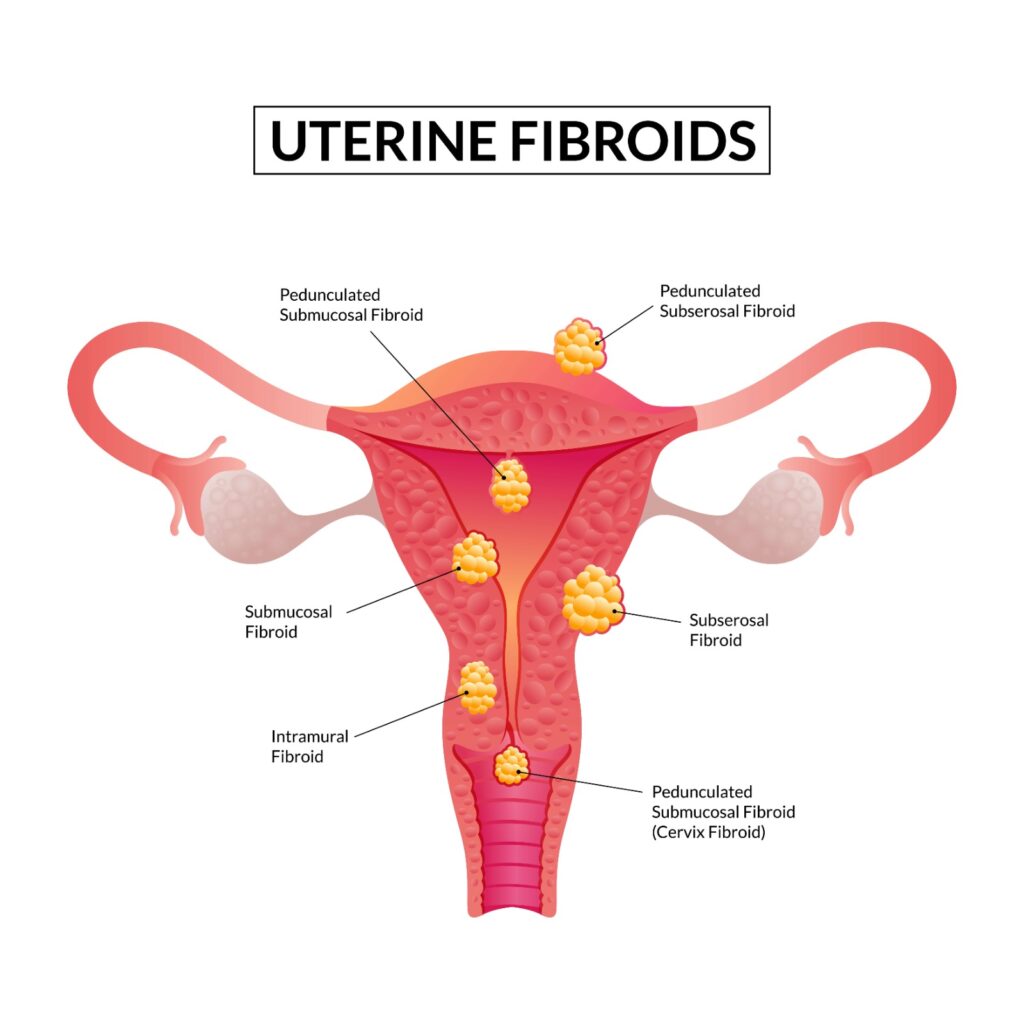
Indications
Surgical intervention for uterine fibroids is considered in the following situations:
Types of Surgical Procedures for Uterine Fibroids
Procedure Steps
Risks and Complications
Recovery and Outlook
Conclusion
Surgical treatment for uterine fibroids is tailored to individual patient needs, considering factors such as symptom severity, desire for fertility, and overall health. It is important for patients to discuss their options thoroughly with a healthcare provider to make informed decisions about their treatment plan. Advances in surgical techniques, including minimally invasive approaches, have improved recovery times and outcomes for many women undergoing surgery for uterine fibroids. Regular follow-up care is essential to monitor healing and ensure optimal postoperative recovery.